- Preview
- Baseball Quiz
- Function of a Cognitive Architecture
- Levels of Cognitive Architectures
- Quiz three layers of Watson
- Assumptions of Cognitive Architectures
- A Cognitive Architecture for Production Systems
- Return to the Pitcher
- Action Selection
- Putting Content in the Architecture
- Bringing in Memory
- Exercise: Production System in Action I
- Exercise: Production System in Action II
- Chunking
- Fundamentals of Learning
- Assignment
- Recap
- The Cognitive Connection
Preview
Baseball Quiz
- the point is that the correct answer depends on knowledge about baseball
Function of a Cognitive Architecture
Cognitive agent: a function to mapping history to actions. Precepts -> Action
Levels of Cognitive Architectures
- Hardware /Implementation level
- Algorithm/Symbol Level
- Task / knowledge Level
- levels are interconnected. the lower level provides architecture for higher level and higher level provides content to the lower level. The constrain each other and some time determine each other.
- Most of the AI work deals with Level 2 and level 3.
Quiz three layers of Watson
a physical computer, algorithm contains at least searching function. Task is usually answering certain questions.
Assumptions of Cognitive Architectures

Architecture + Content = Behavior
- Architecture + Content = Behavior
- now, assume we can fix the architecture, then behaviour change then indicates Content change.
- Now given that function of cognitive architecture, then we can say if action changes, then the knowledge change must be the cause. This is a simplification of the understanding of human cognitive.
A Cognitive Architecture for Production Systems
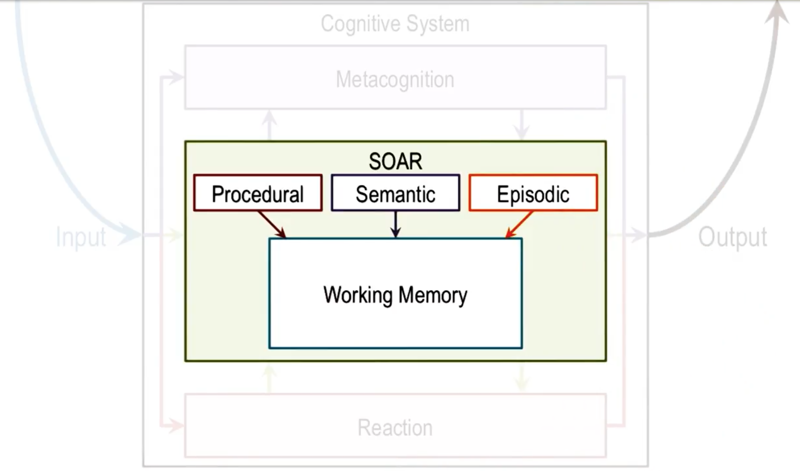
- Episodic: event
- Semantic: generalizations, concept
- Procedural: how to do certain things
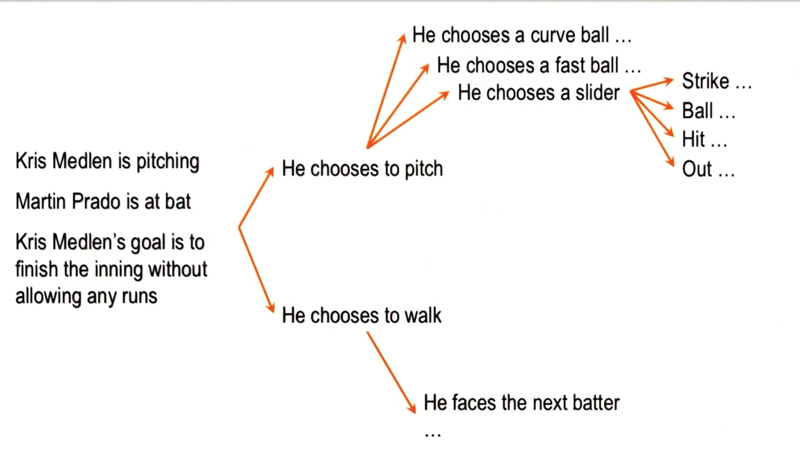
Return to the Pitcher
How AI make decisions on the pitcher problem
- the pitcher has external knowledge: the status of the game of, other players’ position…
- the pitcher also has internal knowledge: his goal
Action Selection
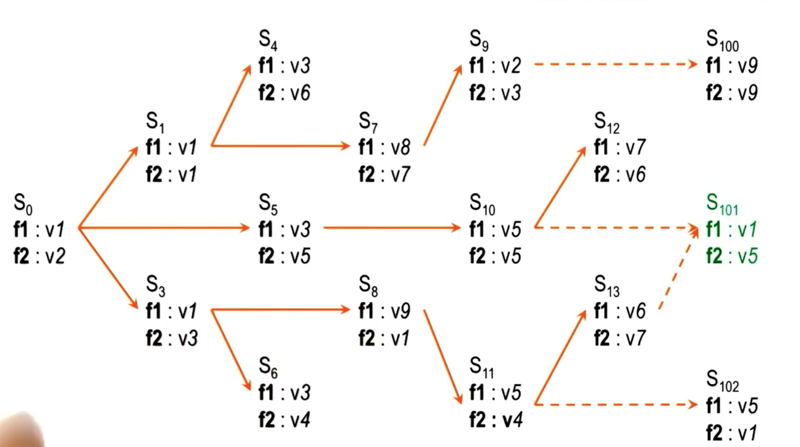
Putting Content in the Architecture

Bringing in Memory
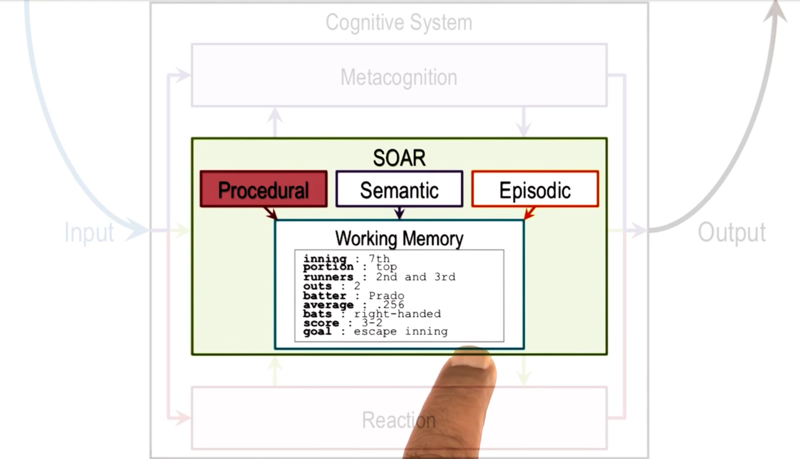

- the internal and external knowledge are in working memory
- procedural rules are long-term memory
Exercise: Production System in Action I

- we mesh the knowledge in working memory (percept) and rules in the procedural type of long-term memory and make the decision on what action to take. This is a P -> A mapping
Exercise: Production System in Action II

- r4 suggests that working memory and long-term memory interact with each other constantly, and new rules,new knowledge and actions can be generated in the process.

- If a new left-handed batter, then two rules can be possible.
- the problem of no action is that there no rule for this particular state.
Chunking
When 2 operators were selected, there is now rule to determine what to do. Then SOAR will have to learn a rule by activating the episodic memory.
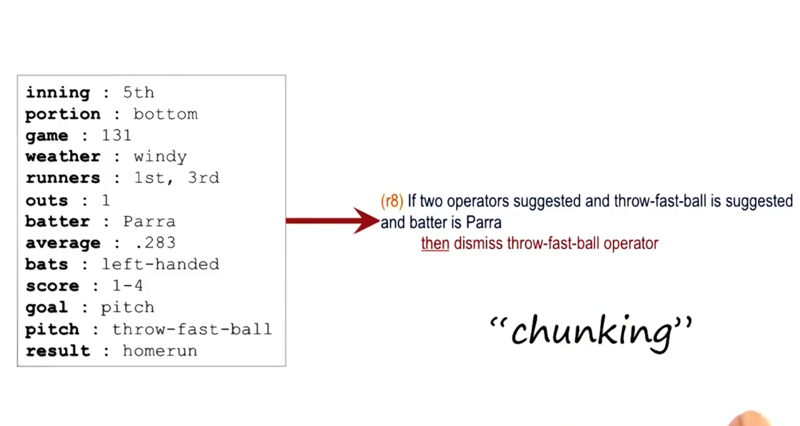
Chunkin is a learning procedure. (for details, see Lehman, J. F., Laird, J. E., & Rosenbloom, P. S. (1996). A gentle introduction to Soar, an architecture for human cognition. Invitation to Cognitive Science, 4, 212-249.)
 Chunking in operation.
Chunking in operation.
Fundamentals of Learning
How do agent learn? when to learn, what to learn, why to learn.
Assignment

Recap

The Cognitive Connection
- working memory in both human and production systems have capacity limitations
- Soar and human have similarity when solving algebra problems
20170202 first draft